Introduction:
The Torus Palatinus is a fibrous mass that projects from the midline of the hard palate. We will show Torus Palatinus Pictures where you can see It is located between the palatine raphe (a ridge of mucous membrane that extends from the hard palate to the soft palate) and the incisive papilla (a minor papilla located between the incisor and canine teeth).
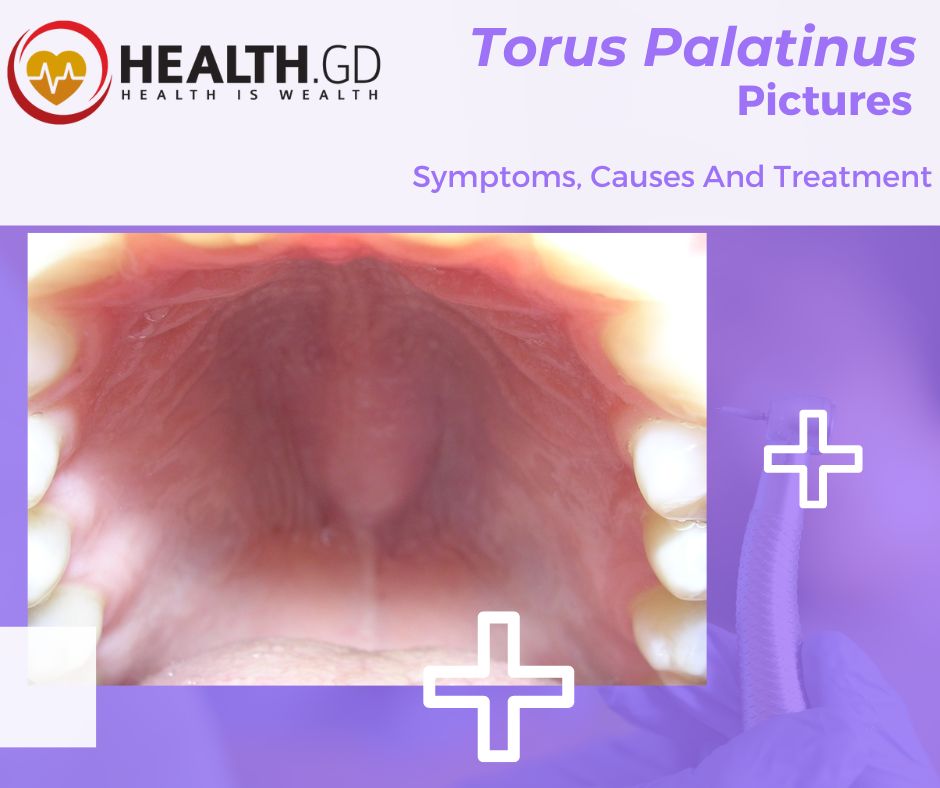
The torus palatinus is also referred to as a palatine torus, palatal Torus, or palatal exostosis.
TORUS PALATINUS appears in a bony prominence, i.e., the areas of bone close to the skin’s surface at the middle of the hard palate.
As you can see in Torus Palatinus Pictures, it enlarges in size from very large and flat to very noticeable.
The oral exostoses are not a sign of disease, but if they become abnormally large, it can create a problem and lead to sore spots.
Moreover, it does not cause any harm or hurt.
However, it is a bony outgrowth at the mouth’s hard palate.
It is found in women primarily; according to studies, about twenty to thirty percent of people have this.
Torus Palatinus is common hyperostosis.
However, it develops in women more than men.
The people of Eskimos, Norwegians, and Americans have found Torus Palatinus more.
Children also have these bony outgrowths, yet it is rare in children.
Age is the main factor.
Also, it primarily develops in young adults and before thirty years.
Genetic, diet, and environmental factors are essential in having Torus Palatinus. The extra bony nodule sometimes develops at the central position at the mouth’s hard palate.
The additional part is down into the oral cavity.
Torus Palatinus have different sizes and shapes as per Torus Palatinus Pictures —the mucous covers bony outgrowth.
Patients are unaware of these outgrowths; however, they seem pale, and sometimes they can have an ulcerated form.
Symptoms Of Torus Palatinus.
Torus Palatinus does not cause pain and harm to a person.
It can vary in size and shape, generally from 2 millimeters to more excellent in size, about 6 millimeters. In Torus Palatinus Pictures it is clearly visible.
It starts to grow slowly.
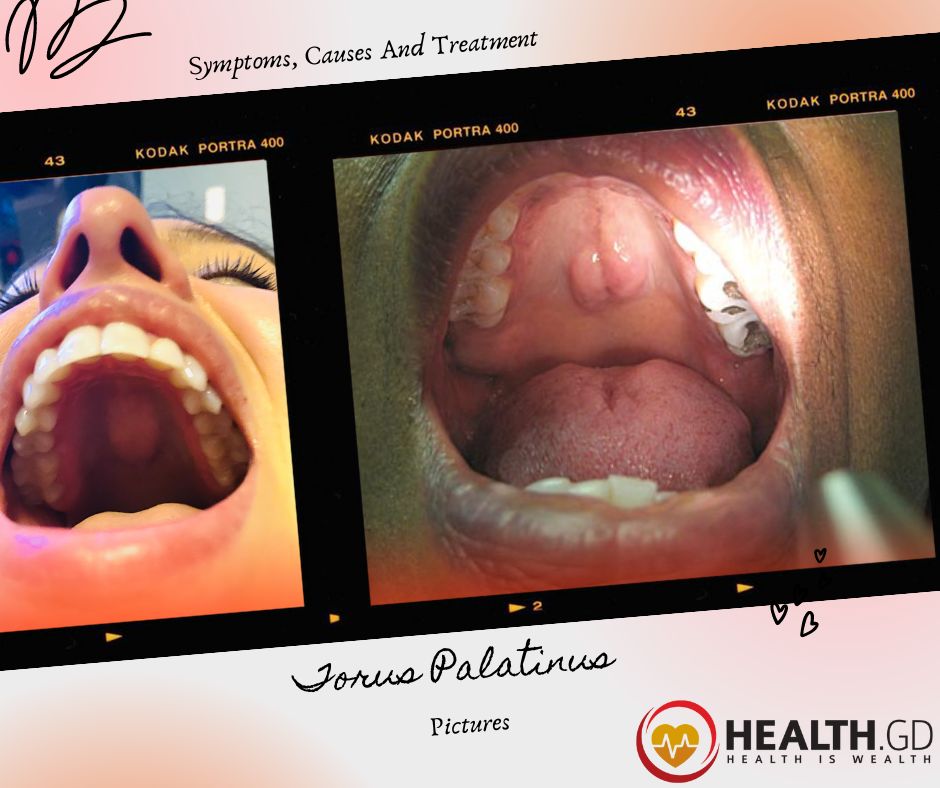
However, it starts at puberty and grows to middle age.
The extended growth is rounded and smooth in shape.
However, it can be a hard lump in some cases.
The lump develops with time, but it grows slowly.
On the contrary, Torus Palatinus can be a life with a person.
Moreover, it is one or more bony growths at the mouth.
It is harmless and does not cause pain; however, it causes difficulty swallowing, chewing, and fitting the dentures.
Torus Palatinus also causes a problem providing the mouth guards to fit in correctly.
These are hard bony outgrowth at the top of the mouth.
Yet these are painless but cause difficulties in getting food like chewing, swallowing, and sometimes food blocks near the bumps.
Moreover, orthodontic devices cause problems in fitting in.
While speech changes patterns, Torus Palatinus causes difficulties.
Dentures on the roof of the mouth can also not fit correctly.
Symptoms not for Torus Palatinus include fever and gums becoming swelling, the other outgrowths on the different body parts.
The bony growth becomes painful, and other signs of illness are expressed, like tooth decay, gum pain, or swollen gum.
It can take different shapes, for example, spindle, nodular, and flat. Sometimes, it shrinks with time but if not, consult a doctor.
Causes of Torus Palatinus.
It is not precisely assured by the researchers what causes it.
1. Genetic Causes
However, genetic transference of some components that cause torus palatinus into offspring might be the reason for the Torus Palatinus.
There is not a clear consensus on the genetic causes of torus palatinus.
However, some researchers believe that it may be caused by a mutation in the gene that encodes keratin 14 (KRT14).
This gene is responsible for producing a type of protein that helps make up epithelial cells’ structural scaffolding.
Mutations in this gene have been linked to several different conditions. One of them is pachyonychia congenital (a condition characterized by thickened nails).
The other one is palmoplantar keratoderma (a condition that causes thickening of the skin on the palms of the hands) and the soles of the feet).
2. Diet:
A diet consisting of carbohydrates and sugars is not a healthy diet. A diet high in refined carbohydrates and sugars can cause torus palatinus.
3. Age:
The soft palate and uvula can sag and become floppy as people age, and this can cause the torus palatinus to become less pronounced.
4. Consuming Saltwater Fish:
Saltwater fish are often thought of as a healthier alternative to freshwater fish. While they can be a good source of protein and omega-3 fatty acids, they can also contain high levels of mercury.
Avoid high-mercury fish, such as swordfish, shark, tilefish, and king mackerel.
According to researchers, saltwater fish can cause this bony outgrowth.
Countries such as Japan, Croatia, and Norway have more probability of this because Saltwater fish have polyunsaturated fats and vitamin D.
5. Teeth grinding and clenching.
Teeth grinding and clenching, also called bruxism, is a condition in which you grind, gnash or clench your teeth.
If you have bruxism, you may unconsciously clench your teeth when you’re awake (awake bruxism) or clench or grind them during sleep (sleep bruxism).
Teeth grinding can be noisy enough to wake your sleep partner. Over time, teeth grinding can damage your teeth and cause other problems. But treatments and changes in your habits may help.
Teeth grinding and clenching can be caused by stress, misaligned teeth, an abnormal bite, or teeth clenching during the day. It can also be caused by sleep disorders such as apnea.
Teeth grinding and clenching are likely to develop Torus Palatinus.
6. Other Reasons:
Other reason includes
- Increase in bone density
- grinding of teeth
Moreover, according to studies, white postmenopausal with moderate-to-large Torus Palatinus were more credible than others to have normal-to-high bone density. The dentist can find it during oral checkups.
However, it can feel like when it is a significant but small bony outgrowth, often not judged by the person.
Oral hygiene recommendations for Torus Palatinus
Oral hygiene is essential for people of all ages. Good oral hygiene habits can help prevent cavities, gum disease, and bad breath.
The following are some oral hygiene recommendations:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a toothbrush that has soft bristles.
- Use toothpaste that contains fluoride.
- Floss your teeth at least once a day.
- Eat a balanced diet and avoid sugary snacks.
- Visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and checkups.
When do You need to see a doctor?
If you have a torus palatinus, you will usually not need to see a dentist or other healthcare provider unless you have signs or symptoms that concern you. Signs and symptoms that may indicate a problem with a torus palatinus include:
- Changes in the size, shape, or color of the torus palatinus.
- Swelling or tenderness in the torus palatinus.
A foul-smelling or bad-tasting
A foul-smelling or bad-tasting discharge from the torus palatinus can indicate an infection. You should see a doctor immediately if the release is accompanied by pain, swelling, or redness.
Difficulty or pain when eating or drinking.
The torus palatinus is the raised fleshy tissue on the roof of the mouth.
It is not uncommon for people to have difficulty eating or drinking from the torus palatinus.
It is because the torus palatinus can get in the way of the teeth, making it difficult to bite down on food.
Additionally, the torus palatinus can make it difficult to suck on a straw or drink from a cup.
If you have difficulty eating or drinking from the torus palatinus, you may want to see a dentist or oral surgeon to have it removed.
Difficulty speaking or difficulty making certain sounds
The torus palatinus is a bony growth that can occur on the palate (roof of the mouth). This growth can cause difficulty speaking due to the obstruction it creates.
See your dentist or another healthcare provider for an evaluation if you have any of these signs or symptoms.
Treatment of Torus Palatinus.
Torus Palatinus is not a harmful disease.
Surgery of Torus Palatinus
However, surgery suggests if the bumps are causing difficulties in fitting the dentures.
If they are causing problems in eating, chewing, and swallowing the food, causing pain in the nodes, it causes problems in drinking, speaking, and maintaining oral hygiene.
It can stick out when you eat the food of hard texture or while talking.
It scratches out.
The outgrowth, i.e., Torus Palatinus on the hard palate, does not connect with the blood vessels, so it can slowly heal when outgrowths are cut naturally.
The surgery will be performed by a maxillofacial surgeon, i,e A doctor specializing in diagnosing and treating disorders of the mouth, teeth, jaws, and face.
Surgery can proceed in a way the doctor makes an incision on the hard palate and cuts the excessive outgrowth.
Some issues one can face after surgery are tissue infections that might cause bleeding, swelling, or an anesthesia reaction.
However, it can recover in four to five weeks.
It would help if you took the medicines on time, and your food must be of soft texture.
Use anti-infectious or oral antiseptics to avoid the infection.
Saltwater is used to wash the throat to remove the chances of infection of the exposed tissues.
Foods and beverages to avoid for Torus Palatinus: it is generally recommended to avoid hard, crunchy, or sticky foods, as well as very hot or cold drinks, as these can aggravate the condition.
Conclusion
The bony outgrowths on the hard palate do not have many harmful effects.
These are painless bumps and benign, i.e., non, cancerous.
People have this small bony outgrowth, and they do not take it seriously Because it doesn’t harm them.
When there are hard bumps with extensive outgrowth in the hard palate of the mouth, then it is not suitable for your health.
However, severe conditions bring surgery, which is the best option to remove the Torus Palatinus growth.
The large out change can irritate and make it ulcerated for many outgrowths into your body is harmful; however, The hard bumps on the mouth can heal naturally by themselves.
Injuries on the mouth or near it can cause slow healing because of the limited tissue surface.
Unusual shapes and growths can be alarming anywhere in the body.
You might have oral tori if you notice hard bumps in your mouth.
The large mandibular tori can cause obstruction in breathing and also cause snoring and sleep apnea.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What causes torus palatinus?
There is no definitive answer to this question as the condition is not fully understood. Some possible causes include genetics, abnormal bone development, or trauma to the area.
What is a torus palatinus?
Torus palatinus is a bony growth that forms on the mouth’s roof near the tongue’s back. This growth is benign (non-cancerous) and is not typically associated with health problems. Some people may have multiple tori palatini, ranging in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters.
Does torus palatinus go away?
There is no cure for torus palatinus, and the condition is not typically harmful. The growths may become more prominent over time, but they do not cause health problems.
How to get rid of torus palatinus?
There is no known way to get rid of torus palatinus. The growths are benign (non-cancerous) and do not typically cause health problems, so treatment is not necessary.
Can stress cause torus palatinus?
There is no known link between stress and the development of torus palatinus. The condition is not fully understood, but some possible causes include genetics, abnormal bone development, or trauma to the area.
Can torus palatinus become cancerous?
No, torus palatinus is not cancerous. The growths are benign (non-cancerous) and do not typically cause health problems.
Can Torus palatinus cause sinus problems?
There is no known link between torus palatinus and sinus problems. The condition is not harmful and does not typically cause any health problems.
How common is Torus palatinus?
The prevalence of torus palatinus is unknown, but the condition is considered relatively rare.
Is torus palatinus painful?
No, torus palatinus is not typically painful. The growths are benign (non-cancerous) and do not usually cause health problems
Why does my torus palatinus hurt?
There is no known reason why a torus palatinus would hurt. The growths are benign (non-cancerous) and do not typically cause health problems. If you are experiencing pain, you should see a doctor rule out other potential causes.
What does a torus palatinus look like?
Torus palatinus is a bony growth that forms on the roof of the mouth, near the back of the tongue. This growth is benign (non-cancerous) and is not typically associated with health problems. Some people may have multiple tori palatini, ranging in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters.
Can Torus palatinus cause snore?
There is no known link between torus palatinus and snoring. The condition is not harmful and does not typically cause any health problems.
Can torus palatinus grow on the back roof of the mouth?
A torus palatinus can form on the back roof of the mouth, near the back of the tongue. This growth is benign (non-cancerous) and is not typically associated with health problems. Some people may have multiple tori palatini, ranging in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters.
Can you get dentures with a torus palatinus?
Dentures are a type of dental prosthetic used to replace missing teeth. They are custom-made to fit your mouth and can be removable or fixed (permanent). Dentures can be made with or without a torus palatinus. Yes, you can get dentures with a torus palatinus. The growth is benign (non-cancerous) and does not typically cause health problems.
What causes torus palatinus to overgrow?
There is no definitive answer to this question as the condition is not fully understood. Some possible causes include genetics, abnormal bone development, or trauma to the area.








