Introduction
Intellectual impairment prevents a person from learning or living normally. A child with intellectual impairment has several degrees. Learning-disabled children may struggle to express their needs and take care of themselves. Individuals with intellectual disabilities may learn and mature slower than their peers. Children with cognitive problems may take longer to walk, speak, dress, and eat independently. They may struggle in school.
Mental health issues may begin before a child turns 18, or even before birth. It could be caused by a cut, disease, or neurological issue. Many brain-impaired youngsters have no known etiology. Common causes of brain dysfunction include Down syndrome, fetal alcohol syndrome, fragile X syndrome, genetic diseases, birth anomalies, and infections. These occur before birth. Some occur during or after birth. Other causes of brain impairment appear later in life in children. A sickness, a significant brain injury, or a stroke are examples.
What Are Some Symptoms of Intellectual Disability?
If intellectual incapacity is severe, symptoms appear quickly. It may be challenging to predict how young children will evolve. Intellectual impairment manifests in many ways. Children with intellectual impairments may face unique challenges.
- Crawling, sitting, or walking take longer than peers.
- Slow down or have problems talking.
- Memory difficulties
- have problems obeying social norms.
- having problems understanding their actions.
- having difficulties understanding
Causes of Intellectual Disability
Many factors may cause learning or cognitive disabilities. People with it may also have Down or Fragile X syndrome. It may be caused by wheezing, measles, or hemorrhagic meningitis. A childhood head blow or exposure to lead or mercury could also do so. Brain abnormalities, maternal disorders, and environmental causes, including alcohol, drugs, and toxins, may also cause intellectual incapacity. Labor and delivery, pregnancy, and birth issues, including lack of air, may all contribute.
Treatment
Intellectual disability is lifelong. However, early and ongoing treatment may improve the person’s life. Intellectually disabled people frequently have various health or physical issues that make life extremely hard. Kills and needs determine how much assistance intellectually disabled people receive at home, school, work, and in the community. Services for intellectually disabled people and their families may help them participate in society. Many types of assistance may be beneficial, including
- Baby and kid’s aid.
- Extra school assistance.
- Childcare support organizations aid families.
- Helping kids become adults.
- employment programs.
- Adults may take day courses.
- There are different housing options.
- Dealing with cases.
Early intervention programs must identify and assist challenging newborns and children under the 1990 Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA). Any qualifying kid with a handicap, including an intellectual impairment, shall receive free special education and other benefits under federal law.
Family, friends, colleagues, community members, schools, and care systems may also help. A service system employee may provide career guidance. If assisted, intellectually disabled people can be joyful and valuable.
Understanding the connection and related conditions
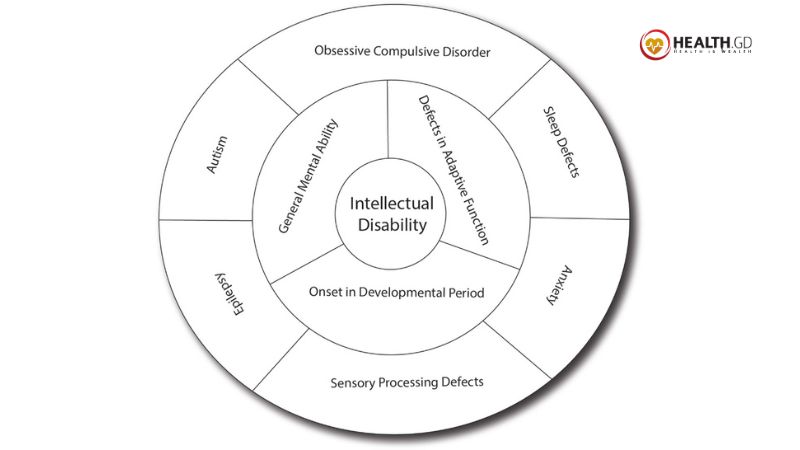
Intellectual impairment typically coexists with mental health, neurodevelopmental, medical, or physical issues. Autism spectrum disorder, cerebral palsy, epilepsy, ADHD, IC, depression, and anxiety are examples. Multiple-condition patients are challenged to discover and diagnose. If someone has problems communicating, depression may be hard to detect. Family caregivers help spot tiny changes. Everyone needs proper examination and treatment to live a healthy and happy life.
Many people think intellectual impairment implies being smarter than their IQ test shows. There’s more to life than IQ. Some people have an average or above-average IQ but struggle with life skills. Many individuals have low IQs but high skills and talents; thus, they do not qualify for intellectual impairment. Or, they have a lower intellectual deficiency than their IQ test indicates.
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fifth edition, text revision (DSM-5-TR) calls intellectual disability “intellectual developmental disorder. This is because many people with intellectual disabilities have brain development issues. If someone under 18 suffers brain damage from a disease, accident, or other cause, it may occur less frequently.
Why Does Intellectual Disability Occur?
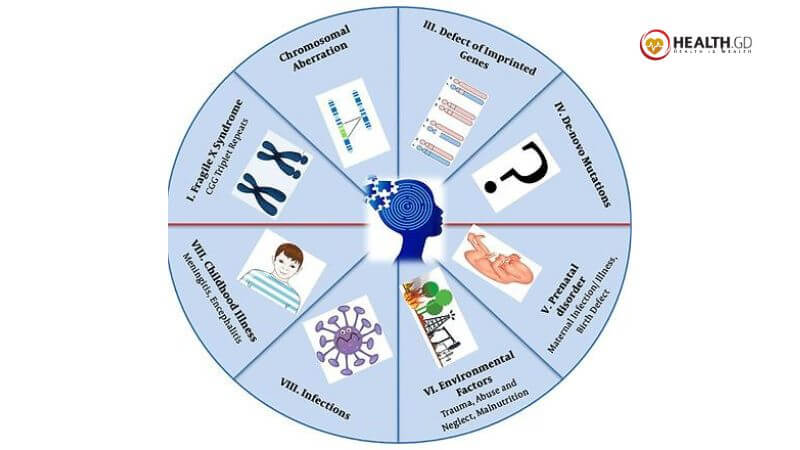
Many factors may cause intellectual issues. Experts believe many causes are typically involved. Intellectual impairment may begin before birth or in early childhood. This has various causes and contributors.
- Genetics and Inheritance: Genetic alterations cause a variety of brain-incapacity illnesses. These anomalies may affect different generations. Examples include Down, Prader-Willi, and Fragile X syndromes.
- Acquiring Infections: Infections such as toxoplasmosis and measles can disrupt fetal development, causing intellectual disabilities like cerebral palsy.
- Birth Malformations: These substances may stunt fetal growth. Marijuana, alcohol, drugs, radiation, and more are examples.
- Various Illnesses: Health issues during pregnancy might impair your baby’s development. They may cause future brain dysfunction. Some hormonal issues include hypothyroidism.
- Accident or Damage: These may cause brain damage and intellectual incapacity.
- Toxic Exposure: Lead and mercury may damage your brain and impair your reasoning.
- Acquiring infections. Mental illness can result from infections of the nervous system, such as measles or meningitis.
- The Brain has tumors: Dangerous and non-cancerous growths count.
- Various illnesses. Seizures with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome may harm the brain. This may cause brain damage.
Types of Intellectual Disability
Some common ones are:
An X chromosomal alteration may cause fragile X syndrome. Speaking, perceiving, and acting properly is difficult for those with this neurological disorder. Two in three Down syndrome patients have intellectual disabilities. This disease causes an extra gene to affect brain and body growth. Down syndrome patients have distinctive physical characteristics that help clinicians identify them. Their neck, ears, hands, and feet may be short, and their eyes may be almond-shaped. They have poor IQs and struggle to grow up.
The uncommon genetic condition Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) affects a child’s intellect and bodily development. This condition is characterized by hyperphagia or constant eating. This causes many affected youngsters to gain weight. Other symptoms include weak muscles, social difficulties, and mental delays.
A pregnant woman who drinks and gives birth may develop fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. However, even small doses of alcohol when pregnant might create problems. FASDs may cause vision, hearing, physical abnormalities, poor IQ, and memory problems. 8
Autism: This cognitive disease makes it difficult to speak, engage, and behave socially.
People believe a combination of hereditary and extrinsic causes caused the illness. Not making eye contact, not wanting to connect, communicating nonverbally, and using sensitive senses are symptoms. Birth issues. If the infant does not receive enough oxygen during delivery or labor, it may not be able to think or reason properly.
Diagnosis of Intellectual Disability
An intellectually disabled individual will struggle with social and functional skills in this scenario. Mental abilities include reading and writing; social skills include communicating with others and solving issues; and actual skills include eating, walking, and dressing.
Beginning before age 18: This condition commonly begins in infancy. Delayed speech, motor skill issues, and memory loss are early indicators.
Researchers have found that 20–35% of people with intellectual disabilities also have anxiety or depression. Your doctor and a team of specialists may order several tests to diagnose your child.
These tests include:
- To detect brain issues, such as an EEG or MRI.
- Genetic screenings may detect brain-impairing illnesses like Fragile X syndrome.
- Based on your child’s symptoms, general medical tests will be conducted.
- Special education assessments
- Development screening exams to assess your child’s intelligence and social skills
- During pregnancy, parents might undergo a prenatal test for development issues.
- Hearing evaluation to determine if the intellectual performance issue is hearing-related, not intellectual impairment.
Different exams and methods may assist with these assessments at any age. Some tests may detect brain disorders in infants. Before the child is old enough for an IQ test and a comprehensive assessment of their adjusted functioning, these tests cannot reveal how terrible it is.



